| Exit Print View | |
Java Platform Micro Edition Software Development Kit Version 3.0, CLDC |

|
Viewing and Editing Project Properties
Running Projects in the Emulator
Searching the WURFL Device Database
Finding Files in the Multiple User Environment
JSR 82: Bluetooth and OBEX Support
JSR 135: Mobile Media API Support
JSR 177: Smart Card Security (SATSA)
JSR 205: Wireless Messaging API (WMA) Support
JSR 211: Content Handler API (CHAPI)
JSR 226: Scalable 2D Vector Graphics
JSR 238: Mobile Internationalization API (MIA)
JSR 256: Mobile Sensor API Support
On a real device, the FileConnection API typically provides access to files stored in the device’s memory or on a memory card.
In the Java ME Platform SDK emulator, the FileConnection API enables MIDlets to access files stored on your computer’s hard disk.
The files that can be accessed using FileConnection are stored in subdirectories of user.home/Application Data /javame-sdk/3.0/work/emulator-instance/appdb/filesystem. For example, the DefaultCldcPhone1 emulator instance comes with a root directory installed called root1, which contains an empty directory named photos. The full path of the file is:
user.home/Application Data /javame-sdk/3.0/work/emulator-instance/appdb/filesystem/root1/photos.
Note - If multiple instances of the same device run simultaneously, the Java ME Platform SDK generates unique file paths for each one. For instance, the first directory is named DefaultCldcPhone1 and the second instance is named DefaultCldcPhone2.
Each subdirectory of filesystem is called a root. The Java ME Platform SDK provides a mechanism for managing roots. While the emulator is running, choose View > External Events Generator from the emulator window’s menu. A utility window opens. Click the File Connection tab.
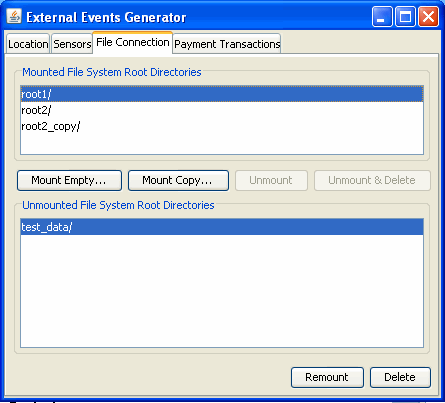
In the File Connection panel you can mount, unmount, or delete filesystem roots. Mounted roots are displayed in the top list, and unmounted roots are moved to the bottom list. Mounted root directories and their subdirectories are available to applications using the FileConnection API. Unmounted roots can be remounted in the future.
To add a new empty filesystem root directory, click Mount Empty and fill in a name for the directory.
To mount a copy of an existing directory, click Mount Copy, and browse to choose a directory you want to copy. When the File System Root Entry dialog opens, enter the name for this root. A deep copy of the selected directory is placed into the emulator’s filesystem with the specified root name.
To make a directory inaccessible to the FileConnection API, select it in the list and click Unmount. The selected root is unmounted and moved to the Unmounted roots list.
To completely remove a mounted directory, select it and click Unmount & Delete.
To remount an unmounted directory, select it and click Remount. The root is moved to the mounted roots list.
To delete an unmounted directory, select it and click Delete. The selected root is removed from the list.